TYPES OF HEARING LOSS
TYPES OF HEARING LOSS
TYPES OF HEARING LOSS
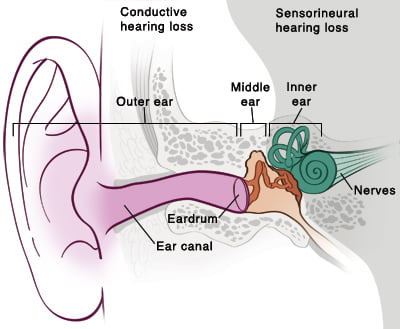
What are the primary types of hearing loss?
The main types of hearing loss vary depending on the affected part of the ear:
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs due to damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, hindering the transmission of sound to the brain.
Conductive hearing loss results from issues in the outer or middle ear and may be treatable through medical or surgical methods.
Mixed hearing loss involves a combination of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss.

What are the primary types of hearing loss?
The main types of hearing loss vary depending on the affected part of the ear:
Sensorineural hearing loss occurs due to damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, hindering the transmission of sound to the brain.
Conductive hearing loss results from issues in the outer or middle ear and may be treatable through medical or surgical methods.
Mixed hearing loss involves a combination of both sensorineural and conductive hearing loss.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss, also known as sensorineural deafness, is the most prevalent form of hearing loss. Individuals with this condition may find sounds unclear or challenging to hear.
Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss The natural aging process (age-related hearing loss or presbycusis)
Prolonged exposure to loud noise (noise-induced hearing loss)
Treatment for Sensorineural Hearing Loss
This type of hearing loss is commonly managed with hearing aids.


Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss, also known as sensorineural deafness, is the most prevalent form of hearing loss. Individuals with this condition may find sounds unclear or challenging to hear.
Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss
The natural aging process (age-related hearing loss or presbycusis)
Prolonged exposure to loud noise (noise-induced hearing loss)
Treatment for Sensorineural Hearing Loss
This type of hearing loss is commonly managed with hearing aids.

Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a disruption in the transmission of sound from the outer or middle ear to the inner ear.
Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss
This type of hearing loss can be caused by blockages in the ear canal, such as earwax or fluid, which prevent sound from reaching the eardrum.
Treatment for Conductive Hearing Loss
Treatment options for conductive hearing loss include removing earwax and addressing the underlying issues through medical or surgical procedures.

Conductive hearing loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when there is a disruption in the transmission of sound from the outer or middle ear to the inner ear.
Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss
This type of hearing loss can be caused by blockages in the ear canal, such as earwax or fluid, which prevent sound from reaching the eardrum.
Treatment for Conductive Hearing Loss
Treatment options for conductive hearing loss include removing earwax and addressing the underlying issues through medical or surgical procedures.
Other Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be further categorized in various ways, including:
High-Frequency or Low-Frequency Hearing Loss: This classification refers to difficulties in hearing specific pitch ranges. High-frequency hearing loss means trouble hearing higher-pitched sounds, while low-frequency hearing loss affects the ability to hear lower-pitched sounds.
Unilateral or Bilateral Hearing Loss: This distinction identifies whether hearing loss affects one ear (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral).
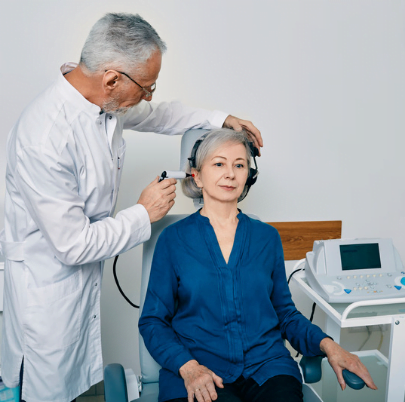

Other Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be further categorized in various ways, including:
High-Frequency or Low-Frequency Hearing Loss: This classification refers to difficulties in hearing specific pitch ranges. High-frequency hearing loss means trouble hearing higher-pitched sounds, while low-frequency hearing loss affects the ability to hear lower-pitched sounds.
Unilateral or Bilateral Hearing Loss: This distinction identifies whether hearing loss affects one ear (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral).

Other Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be further categorized in various ways, including:
Progressive or Sudden Hearing Loss: This describes the rate at which hearing loss occurs, either gradually over time (progressive) or rapidly (sudden).
Acquired or Congenital Hearing Loss: This differentiation indicates whether hearing loss was present at birth (congenital) or developed later in life (acquired)

Other Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be further categorized in various ways, including:
Progressive or Sudden Hearing Loss: This describes the rate at which hearing loss occurs, either gradually over time (progressive) or rapidly (sudden).
Acquired or Congenital Hearing Loss: This differentiation indicates whether hearing loss was present at birth (congenital) or developed later in life (acquired)
Did you know?
FAQS TYPES OF HEARING LOSS
The main types of hearing loss are sensorineural, conductive, and mixed hearing loss. Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, conductive hearing loss occurs when sound cannot pass through the outer or middle ear, and mixed hearing loss is a combination of both.
Sensorineural hearing loss is usually permanent and occurs when there is damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, often due to aging, noise exposure, or genetics. Conductive hearing loss, on the other hand, is often temporary and occurs when sound waves cannot reach the inner ear, typically due to blockages like earwax or fluid buildup.
Yes, hearing loss can affect one ear (unilateral) or both ears (bilateral). The impact on each ear may vary, and the treatment approach can differ depending on whether the hearing loss is unilateral or bilateral.
Sensorineural hearing loss often results in difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments, and a perception that people are mumbling. Conductive hearing loss may cause muffled hearing, ear pain, or a feeling of fullness in the ear. Mixed hearing loss combines symptoms from both types.
Hearing loss is diagnosed through a comprehensive hearing test conducted by an audiologist. This test will measure your ability to hear different frequencies and volumes and help determine the type and degree of hearing loss you may have. Based on the results, the audiologist will recommend the most appropriate treatment.





