LEVEL OF HEARING DIFFICULTY
LEVEL OF HEARING DIFFICULTY

LEVEL OF HEARING DIFFICULTY

Compare levels of hearing loss
Hearing loss severity is typically assessed in two ways:
Loudness: How loud must a sound be for you to hear it?
Pitch: Which frequencies are challenging for you to detect?
Below are the main categories of hearing loss, with examples of sounds that may be inaudible at each level, based on their loudness and pitch.

Compare levels of hearing loss
Hearing loss severity is typically assessed in two ways:
- Loudness: How loud must a sound be for you to hear it?
- Pitch: Which frequencies are challenging for you to detect?
Below are the main categories of hearing loss, with examples of sounds that may be inaudible at each level, based on their loudness and pitch.

Compare levels of hearing loss
Hearing loss severity is typically assessed in two ways:
- Loudness: How loud must a sound be for you to hear it?
- Pitch: Which frequencies are challenging for you to detect?
Below are the main categories of hearing loss, with examples of sounds that may be inaudible at each level, based on their loudness and pitch.
Level of hearing loss
Normal hearing
Mild hearing loss
Moderate hearing loss
Severe hearing loss
Profound hearing loss
Decibel
≤20 dB
21-40 dB
41-70 dB
71-95 dB
≥95 dB
Symptoms
Sounds you are missing
No sounds missing
Ticking clock
Vacuum cleaner
Baby crying
Aeroplanes
Level of hearing loss
Normal hearing
Mild hearing loss
Moderate hearing loss
Severe hearing loss
Profound hearing loss
Decibel
≤20 dB
21-40 dB
41-70 dB
71-95 dB
≥95 dB
Symptoms
Sounds you are missing
No sounds missing
Ticking clock
Vacuum cleaner
Baby crying
Aeroplanes
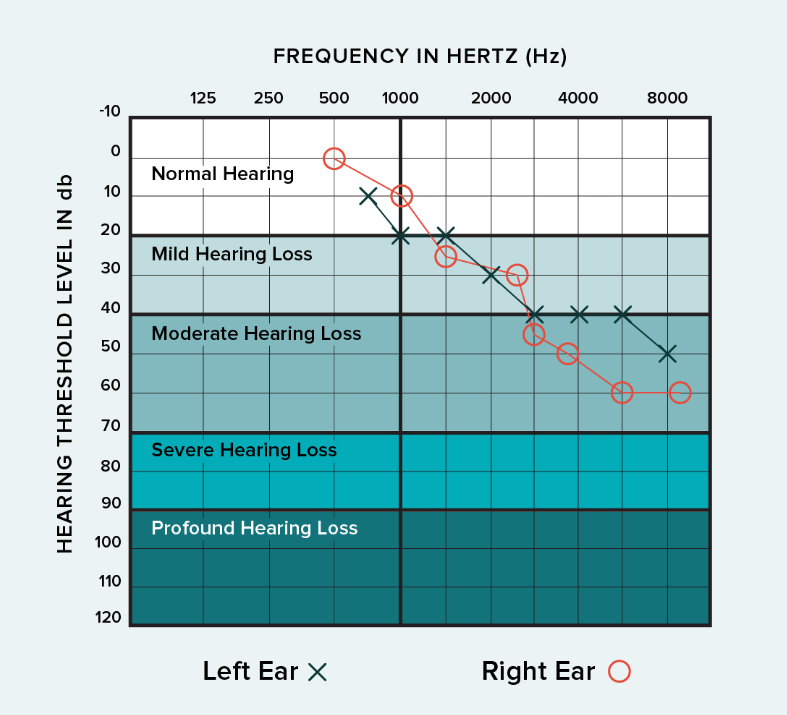
Reading an audiogram
An audiogram is a chart that presents the results of your detailed hearing test.
The X-axis represents different sound frequencies, arranged like piano keys, with low pitches on the left and high pitches on the right.
The Y-axis indicates loudness, increasing downward on the graph. The plotted points show the volume required for you to hear each pitch during the test.
Red circles denote your right ear, while blue crosses represent your left ear.
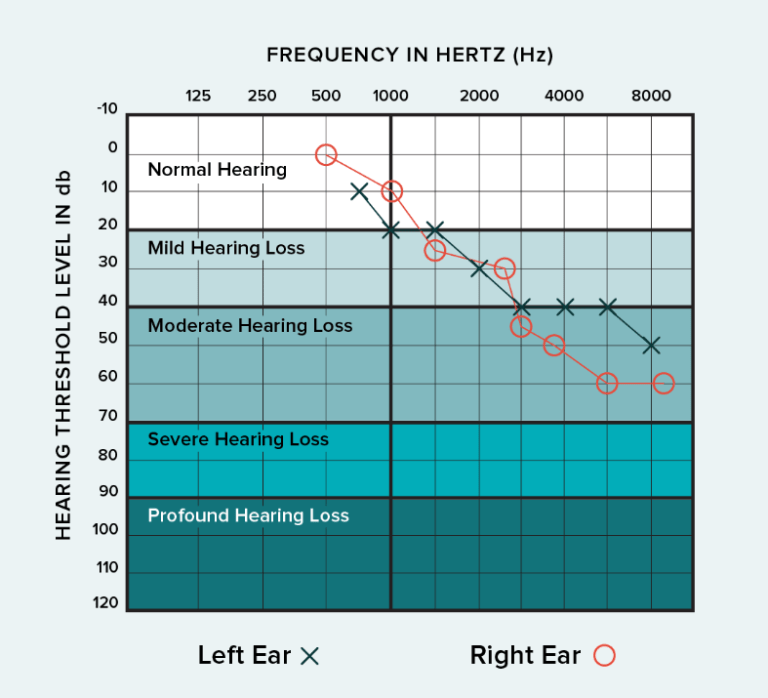
Reading an audiogram
An audiogram is a chart that presents the results of your detailed hearing test.
- The X-axis represents different sound frequencies, arranged like piano keys, with low pitches on the left and high pitches on the right.
- The Y-axis indicates loudness, increasing downward on the graph. The plotted points show the volume required for you to hear each pitch during the test.
Red circles denote your right ear, while blue crosses represent your left ear.
Did you know?

Free Home Visits
Experience the convenience of professional hearing care in the comfort of your own home.

Guaranteed Price Match
Find a better price elsewhere? We’ll match it to ensure you get the best deal.

60 day money back Guarantee
Try our services risk-free with our no-questions-asked 60-day money-back guarantee.

Free Home Visits
Experience the convenience of professional hearing care in the comfort of your own home.

Guaranteed Price Match
Find a better price elsewhere? We’ll match it to ensure you get the best deal.

60 day money back Guarantee
Try our services risk-free with our no-questions-asked 60-day money-back guarantee.

Free Home Visits
Experience the convenience of professional hearing care in the comfort of your own home.

Guaranteed Price Match
Find a better price elsewhere? We’ll match it to ensure you get the best deal.

60 day money back Guarantee
Try our services risk-free with our no-questions-asked 60-day money-back guarantee.
FAQS LEVELS OF HEARING LOSS
Hearing loss is categorized into mild, moderate, severe, and profound levels based on the extent of impairment. Each level reflects the degree to which hearing ability is affected.
Severity is measured by assessing the loudness (how loud sounds must be for you to hear them) and pitch (which frequencies are difficult for you to hear) on an audiogram.
At different levels of hearing loss, you may have difficulty hearing specific sounds, ranging from conversational speech to louder environmental noises, depending on the severity and frequency.
Hearing aids amplify sounds to match the severity of your hearing loss, improving your ability to hear at various frequencies and loudness levels. They can be customized to fit your specific hearing needs and preferences.
Yes, hearing loss can change due to factors such as aging, noise exposure, or medical conditions. Regular hearing evaluations can track any changes in your hearing ability.





